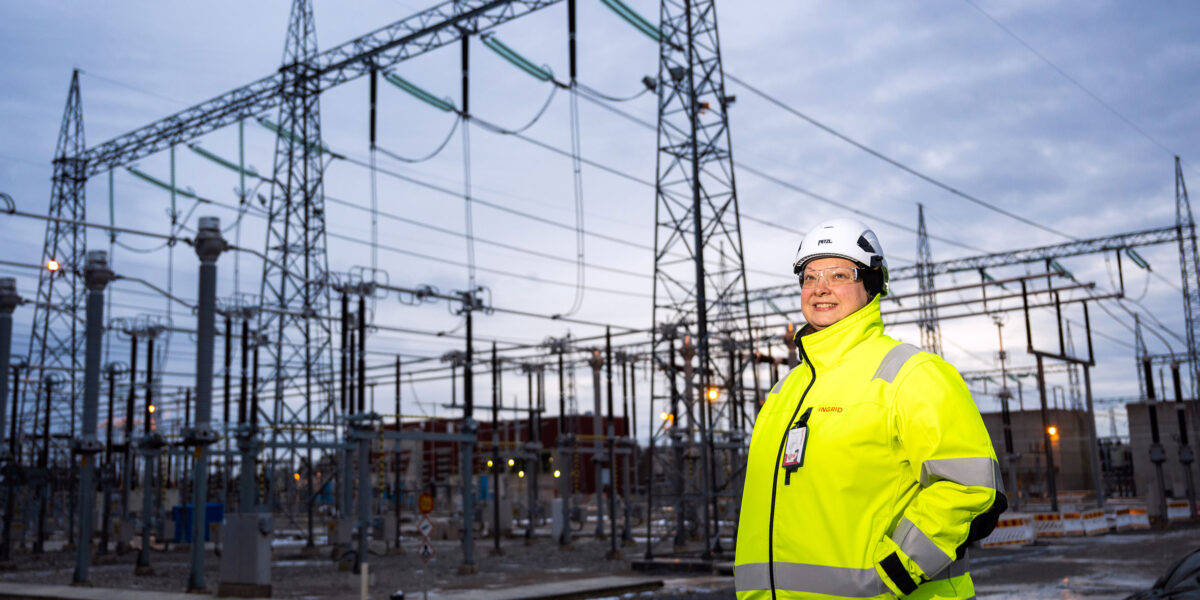
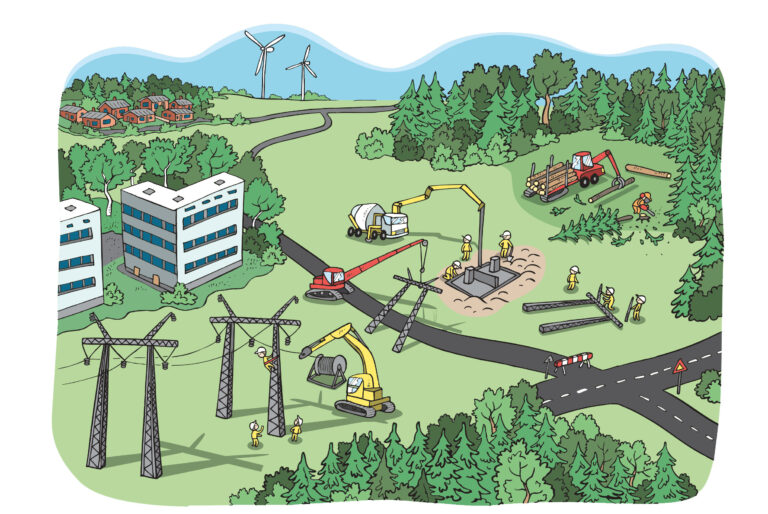
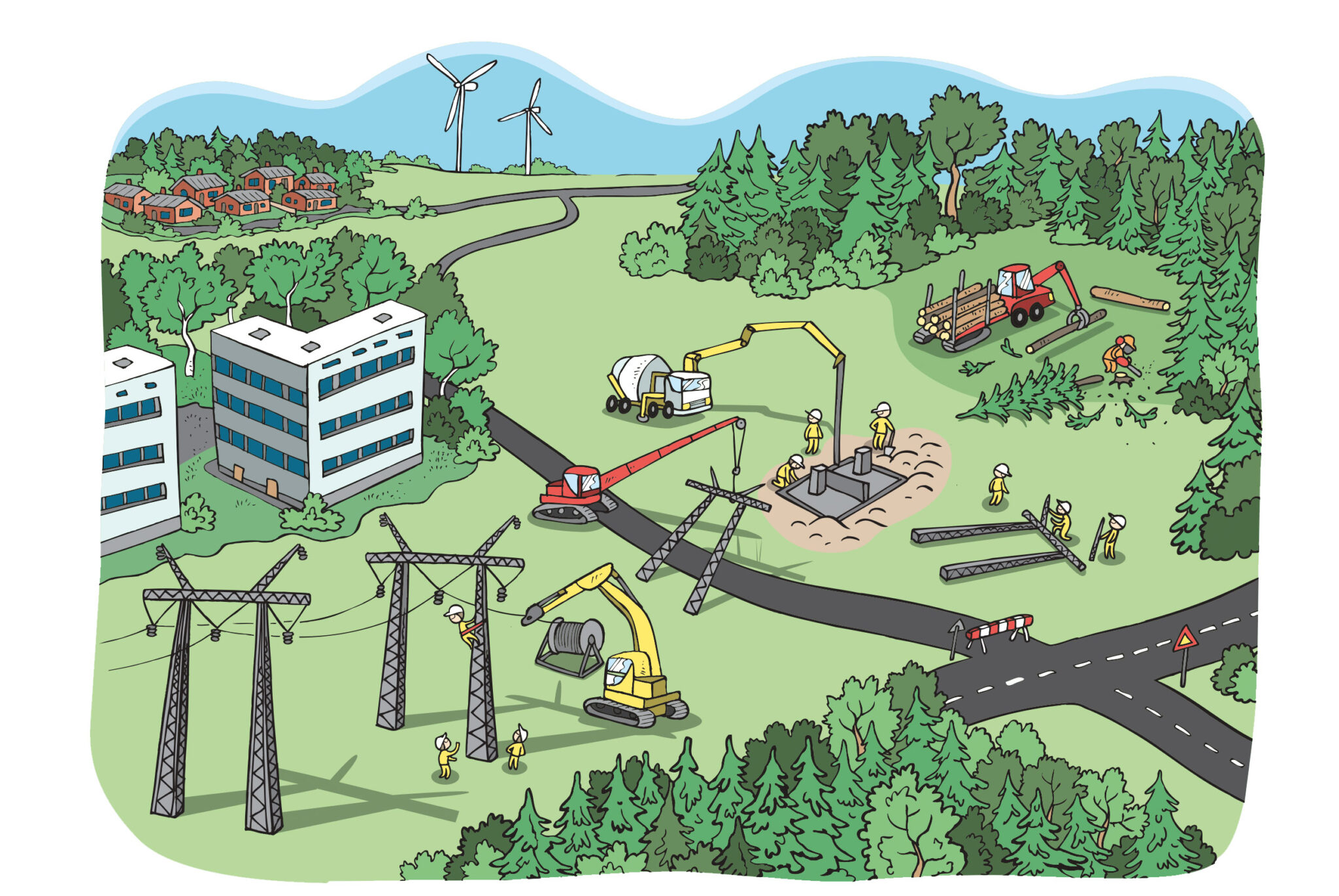
Commissioning takes place in Fingrid’s various projects almost weekly throughout Finland.
The work starts already before the actual commissioning date, which means that Maria Nortema, Expert, Grid Operation in the Southwest Finland region for Fingrid, has planning meetings with the contractor.
Prior to the commissioning date, it is ensured that the required documentation is in order and the installation has been tested.
“Fingrid is responsible for monitoring the construction of substations and transmission lines, while contractors carry out the actual construction and installation work. Collaboration begins in the early stages of the project and remains close throughout the construction and subsequent commissioning,” Nortema says.
A commissioning programme is prepared for each project together with the contractor and reviewed point-by-point on the commissioning date.
The first step is to review the documentation required for commissioning, such as the signed commissioning inspection records, completed installation inspection records, and deficiency lists. A visual inspection is then carried out to ensure, for example, that the additional earthing has not been left connected and that all excess items have been removed from the area.
Main grid control centre leads commissioning
Once it has been confirmed that everything corresponds to the requirements of the outage order, Fingrid’s grid operation specialist grants the main grid centre permission for commissioning.
The operator at the main grid control centre remotely controls the substation’s switchgear according to the switching schedule one switch device at a time using the power control system. During switching, the switching supervisors and the switching operator remain in contact by phone.
“The local switching specialist is the operator’s eyes and ears at the substation.”
“The switching operator is the switching supervisor’s eyes and ears at the station. If the power control system receives alarms from the substation during switching, switching is suspended and the situation is resolved before continuing,” Nortema says.
The commissioning of a new transmission line or substation affects the entire grid. That is why outage planning is especially important for large projects with multiple commissioning phases.
Planning assesses which work stages require outages and determines the duration of the outage and the impact on customers. A precise schedule of work and outages is prepared well in advance of construction work.
“The need for outages at substations varies depending on whether it is a new ‘green field’ station or a renovated substation. Transmission outages for new builds are usually simpler and shorter in duration. On the other hand, renovated substations require more bay and transmission line interruptions as the work progresses. They can take several weeks per transmission line,” Nortema says.
Reliable and safe electricity
When planning the operation of Fingrid’s power system, the commissioning of a new substation or transmission line is prepared by studying the procedures and outages required.
Outages are coordinated at a suitable time together with the grid operation specialist in the area. In addition, a busbar division is specified for the new substation. Planning of the busbar division is an essential part of commissioning that affects the reliability of the substation. It defines how loads are distributed between busbars and reduces the impact of a fault on the grid.
“A substation’s core usually has one or more busbars through which the power transmitted by transformers and transmission lines is transmitted to customers or the next substation. A well-planned busbar division is a prerequisite for maintaining sufficient reliability in the grid and delivering electrical energy to customers safely and reliably,” explains Joni Järvinen, Specialist, Transmission Management, at Fingrid.
A new substation or transmission line typically increases the transmission capacity or reliability in its impact area. Operational planning ensures that the new section of the grid has been through calculation models and provides the intended benefits, either in the form of higher transmission capacity or better reliability.